- Welcome to “Naijaclass Academy“, where you can get the correct solved WAEC 2025 Geography question and answer for Objective, Essay a day before the exam.
Waec 2025 Geography Question And Answer

Thursday, 29th May 2025
Geography 2 (Essay): 9:30am – 11:30am
Geography 1 (Objective): 11:30am – 12:30pm
GEOGRAPHY OBJ
01-10: CBACBBBCCB
11-20: ABBDACCDBA
21-30: BBDCCCBADA
31-40: BABDABDBDA
41-50: CACACCACBD
COMPLETED
USE THIS
COMPLETED.
Answer four questions in all two questions from each of Sections A and B.
SECTION A
*WAEC GEOGRAPHY*
*NUMBER ONE*
(1a)
(PICK ANY FIVE)
(i) Rapid population growth due to rural-urban migration.
(ii) High population density in residential and commercial areas.
(iii) Presence of informal settlements or slums with poor living conditions.
(iv) Inadequate infrastructure and services such as water, sanitation, and electricity.
(v) Diverse economic activities including formal and informal sectors.
(vi) High unemployment and underemployment rates.
(vii) Traffic congestion and poor transport systems.
(viii) Social problems like crime, poverty, and inadequate healthcare.
(1b)
(PICK ANY FIVE)
(i) Food Supply: Urban settlements rely heavily on rural areas for food such as crops and vegetables. Since cities have limited space for farming, rural farmers provide the essential food needed to feed the growing urban population.
(ii) Raw Materials for Industries: Many urban industries depend on raw materials sourced from rural areas. For example, cotton, timber, minerals, and other agricultural products harvested in rural areas are processed in urban factories.
(iii) Labor Migration: Rural areas supply labor to urban settlements. Many people migrate from rural to urban areas seeking employment, thus providing workers for various jobs in industries, construction, and services in the cities.
(iv) Water Resources: Urban centers often rely on rivers, lakes, and underground water sources found in rural regions to meet their water needs for drinking, sanitation, and industrial use.
(v) Energy Resources: Many urban areas depend on fuelwood, charcoal, and other traditional energy sources collected or produced in rural areas, especially where modern energy supplies are limited.
(vi) Markets for Urban Goods: Rural populations form an important market for goods produced in urban areas. Manufactured goods, clothing, and electronics made in cities are often sold to rural consumers.
(vii) Livestock Products: Rural areas provide meat, milk, hides, and other animal products to urban centers, supporting urban food consumption and industrial needs.
(viii) Cultural and Social Links: Urban and rural areas are linked through family ties, traditions, and social networks. People often maintain cultural practices and support systems that connect city dwellers with their rural origins, fostering social cohesion.
OR
(1a)
(i)Rapid population growth: Developing countries often experience high rates of urbanization as people migrate from rural areas to cities in search of opportunities.
(ii)Informal settlements:
Due to rapid urbanization and lack of affordable housing, many urban areas in developing countries have a significant presence of informal settlements or slums.
(iii)Inadequate infrastructure: Urban areas in developing countries often struggle with inadequate infrastructure, including limited access to clean water, sanitation, electricity, and transportation.
(iv)High levels of unemployment and
poverty: Despite the opportunities that cities offer, many urban residents in developing countries face high levels of unemployment and poverty.
(v)Social and economic
inequalities: Urban areas in developing countries often exhibit significant social and economic inequalities, with disparities in access to resources, opportunities, and services.
(1b)
(i)Food supply: Urban areas depend on rural settlements for their food supply, as rural areas are often the primary producers of agricultural products.
(ii)Labor force: Rural areas often provide a labor force for urban industries and services, as people migrate from rural areas to cities in search of employment.
(iii)Natural resources: Urban areas depend on rural areas for natural resources, such as water, timber, and minerals.
(iv)Recreation and tourism: Rural areas often provide recreational and tourist opportunities for urban residents, offering a break from the hustle and bustle of city life.
Cultural and social
(v)connections: Urban areas often maintain cultural and social connections with surrounding rural areas, as many urban residents have family and cultural ties to rural communities.
=================================================
*WAEC GEOGRAPHY*
*NUMBER TWO*
(2a)
The balance of trade is the difference in value between a country’s exports and imports of goods over a specific period. If a country exports more than it imports, it has a favorable balance of trade (trade surplus), if it imports more than it exports, it has an unfavorable balance of trade (trade deficit).
(2b)
(PICK ANY FIVE)
(i) Availability of raw materials in Tropical Africa needed by industries in developed countries.
(ii) Demand for manufactured goods from developed countries by African consumers.
(iii) Improved transport and communication systems linking the regions.
(iv) Trade agreements and partnerships between African nations and developed countries.
(v) Technological advancement in shipping and logistics.
(vi) Globalization and liberalization of markets.
(vii) Investment by developed countries in African mining and agricultural sectors.
(viii) Colonial ties and historical trading relationships.
(2c)
(PICK ANY FOUR)
(i) It earns foreign exchange through exports.
(ii) It creates employment opportunities in various sectors.
(iii) It encourages the development of infrastructure such as ports, roads, and communication networks.
(iv) It leads to the transfer of technology and skills.
(v) It promotes industrial and agricultural growth.
(vi) It enables access to goods and services not produced locally.
===============================================
*WAEC GEOGRAPHY*
*NUMBER THREE*
(3a)
Pipeline transportation is the method of transporting liquids and gases through a system of pipes from one location to another. It is commonly used for the movement of petroleum products, natural gas, and water over long distances in a safe, efficient, and continuous manner.
(3b)
(PICK ANY TWO)
(i) Crude oil
(ii) Natural gas
(iii) Petrol (gasoline)
(iv) Diesel
(v) Water
(vi) Liquid chemicals
(3ci)
(PICK ANY FOUR)
(i) It helps to reduce road congestion and traffic accidents.
(ii) It is a cost-effective means of transporting large volumes over long distances.
(iii) It requires less maintenance compared to road and rail transport.
(iv) It provides a steady and uninterrupted flow of products.
(v) It minimizes environmental pollution when well-maintained.
(vi) It reduces the need for storage and handling at multiple points.
(3cii)
(PICK ANY FOUR)
(i) Vandalism and theft often lead to loss of products and damage.
(ii) The initial cost of constructing pipelines is very high.
(iii) Leakages and bursts can cause serious environmental pollution.
(iv) Construction and maintenance are difficult in remote or forested areas.
(v) Pipelines have fixed routes and limited flexibility.
(vi) Communities may be displaced during the laying of pipelines.
=====================SECTION B==========================
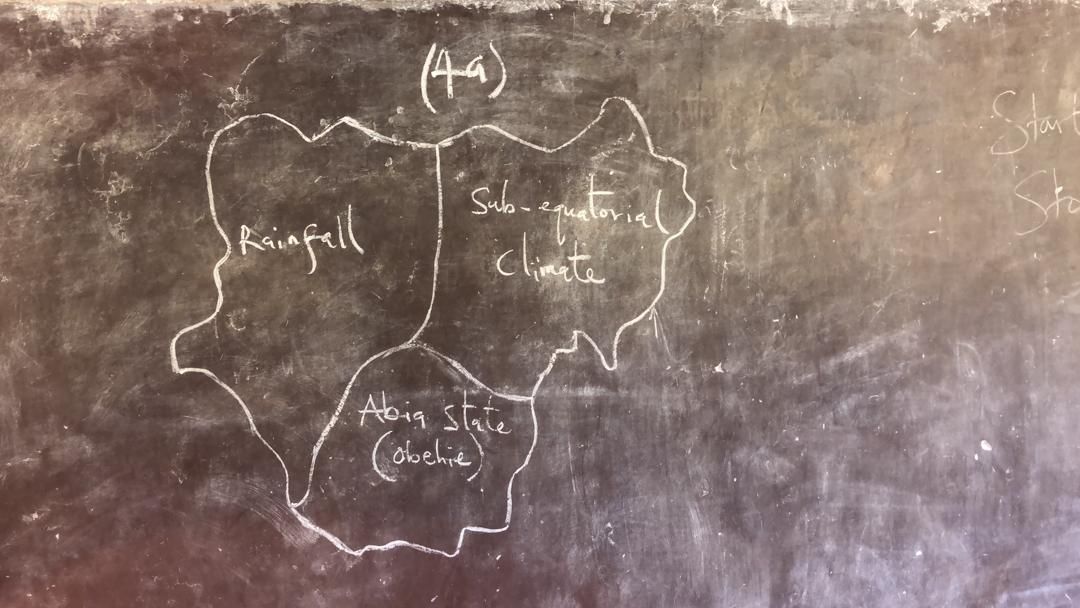
(4a)
Coming
(4b)
(i)Latitude: Areas closer to the equator generally receive more rainfall than those further away.
(ii)Prevailing Winds: The direction and moisture content of winds influence rainfall patterns.
(iii)Altitude: Higher elevations tend to receive more rainfall than low-lying areas.
(iv)Distance from the Coast: Coastal regions receive more rainfall compared to inland areas.
(4c)
(i)High Rainfall: Sub-equatorial regions experience high annual rainfall, often exceeding 1500 mm.
(ii)High Temperatures: Temperatures are consistently high throughout the year.
(iii)Short Dry Season: The dry season is relatively short and less intense compared to other parts of Nigeria
===============================================
*NUMBER FIVE*
(5a)
(i)Latitude: Areas closer to the equator generally receive more rainfall than those further away.
(ii)Prevailing Winds: The direction and moisture content of winds influence rainfall patterns.
(iii)Altitude: Higher elevations tend to receive more rainfall than low-lying areas.
(iv)Distance from the Coast: Coastal regions receive more rainfall compared to inland areas.
(5b)
(i)High Rainfall: Sub-equatorial regions experience high annual rainfall, often exceeding 1500 mm.
(ii)High Temperatures: Temperatures are consistently high throughout the year.
(iii)Short Dry Season: The dry season is relatively short and less intense compared to other parts of Nigeria
*GEOGRAPHY ANSWERS*
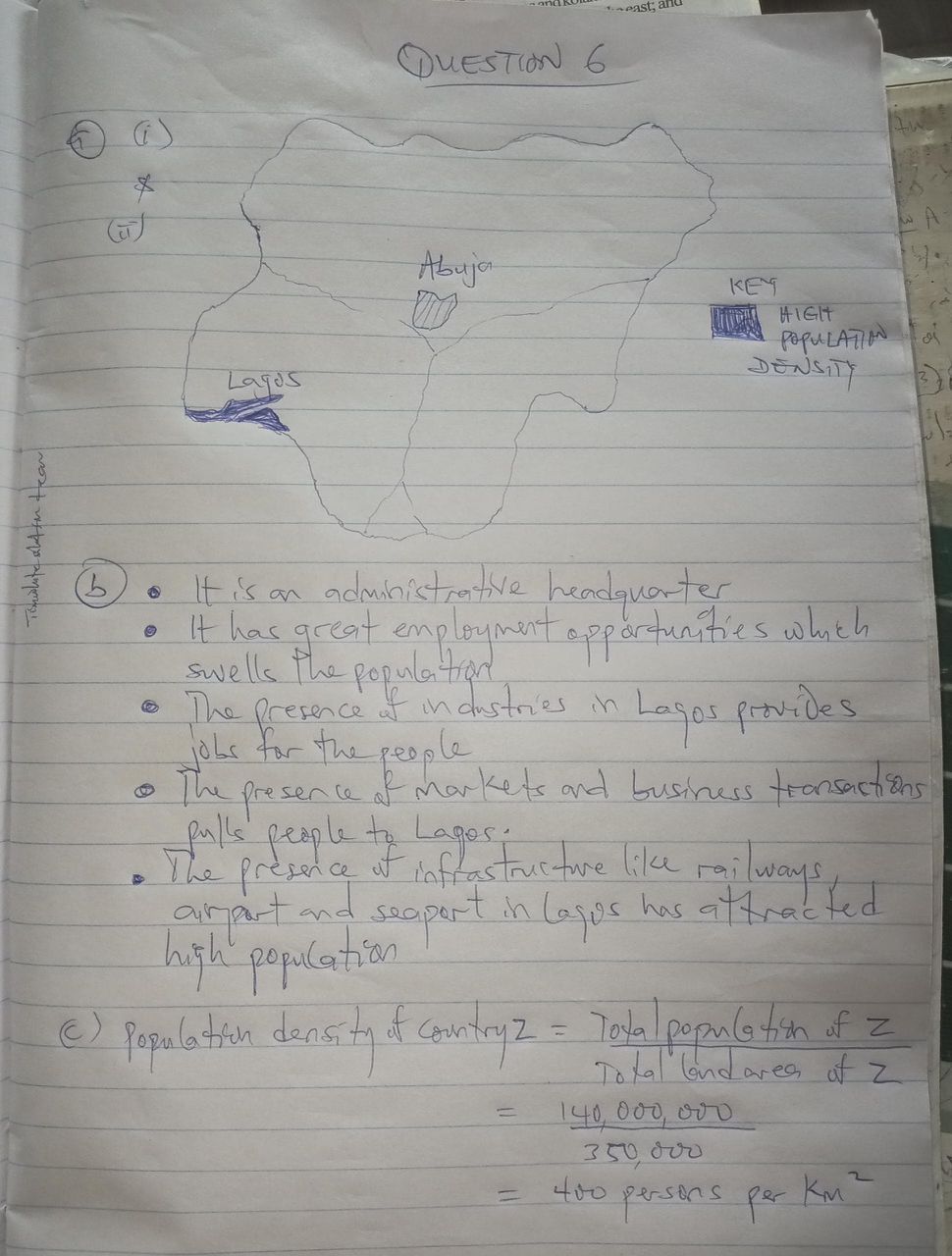
*NUMBER SIX*
(6b)
(i) Economic Opportunities: Areas with high population density often offer more diverse and perceived lucrative economic opportunities in industrial, commercial, and service sectors. This attracts a large number of migrants from rural areas seeking employment and better livelihoods. For instance, Lagos attracts people due to its status as the economic hub of Nigeria.
(ii) Industrial Development: The presence of established industries, manufacturing plants, and commercial activities creates numerous jobs and draws people to these urban centers. These industries provide a magnetic pull for labour.
(iii) Administrative/Political Centres: Capital cities (like Abuja) or major administrative centers attract a large population due to government jobs, administrative functions, and related services, leading to high population concentrations. Even in older urban areas like Ibadan or Kano, their historical administrative significance contributed to their growth.
(iv) Availability of Social Amenities: High-density areas typically have better access to essential social amenities and infrastructure such as better schools, universities, hospitals, recreational facilities, reliable electricity (though often inconsistent), and pipe-borne water, which serve as pull factors for migration.
(v) Historical Significance and Early Urbanization: Some areas have historically been significant trading posts, cultural centers, or political capitals, leading to their early urbanization and continued growth. For example, Kano in the North or Ibadan in the South-West have long histories of large populations.
(vi) Fertile Agricultural Lands (historical for some regions): While not the primary reason for modern high urban density, historically, some areas became densely populated due to exceptionally fertile agricultural lands that supported a large population over centuries, which later transitioned into urban centers (e.g., parts of Kano or the highly agrarian south-eastern regions).
(vii) Coastal or Riverine Location (for some areas): Cities located on coastlines or major rivers benefit from trade, fishing, and port activities, which foster economic growth and attract settlement (e.g., Lagos, Port Harcourt).
(c)
Using
Population Density = Total Population / Total Land Area
Given:
Total Population = 140,000,000 people
Total Land Area = 350,000 km²
Population Density = 140,000,000 / 350,000
Population Density = 1400 / 3.5
Population Density = 400
The population density of Country Z is 400 people per km².





Geography question
Money matter naa i no get pls
Thanks alot
MATHEMATICE ANSWERS
Thank you for this job god help you never for ever
Sir you are wonderful to us sir; in jesus name you will not fall