Looking for Neco 2025 Economics Question and Answer (Objective & Essay) that are correct, verified, and delivered before the exam? You’ve come to the right place. Naijaclass.com is Nigeria’s #1 trusted website for real NECO Economics expo/runs that guarantees success.
We provide students with accurate Economics answers, including full workings, definitions, and explanations to help you pass with A1 – B3 grades.
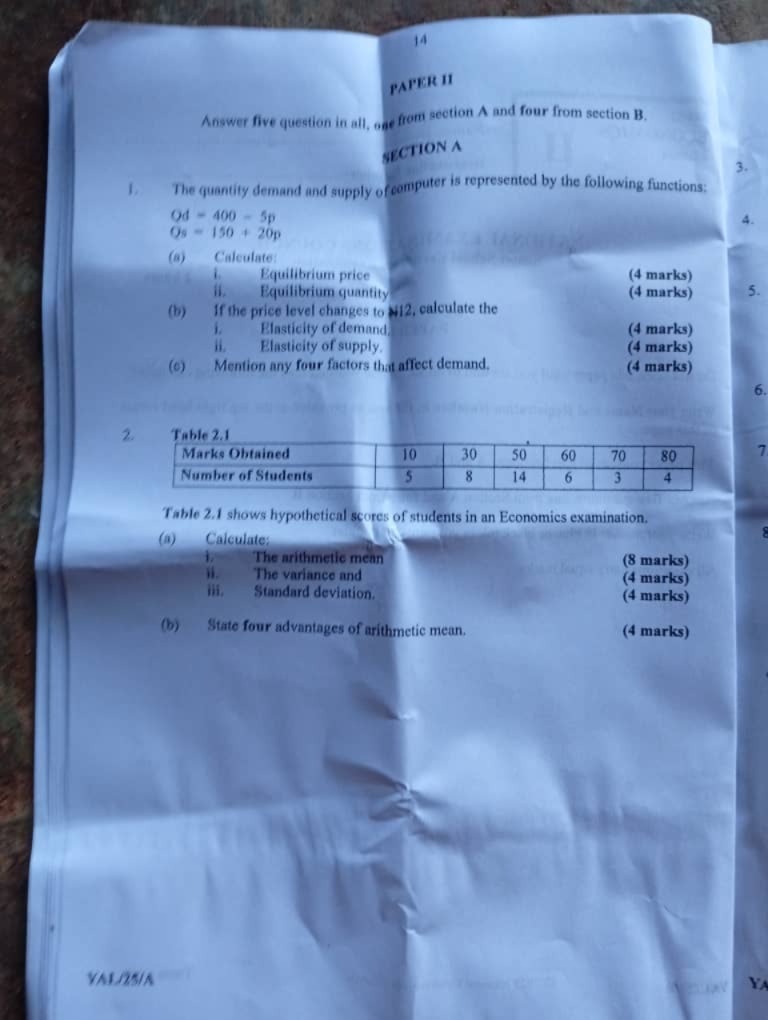
ECONOMICS OBJ
01-10: BECEBEECBD
11-20: CBEEECEDEC
21-30: CCCDDCECBE
31-40: CADAADAADD
41-50: DACBEBAEBE
51-60: DDCDDECDDD
================================================
NUMBER 1

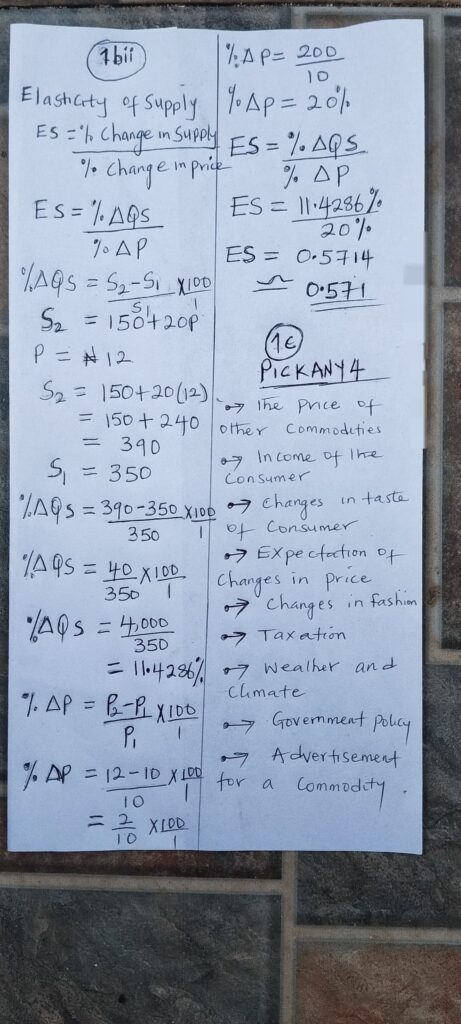
NUMBER 2
(3a)
(i) Transaction Motive: This is the need to hold money for day-to-day expenses such as buying food, transport, and paying bills. Individuals and businesses keep money to carry out regular transactions.
(ii) Precautionary Motive: This is the need to keep money aside for unforeseen situations like emergencies, sickness, accidents, or unexpected expenses. People hold money “just in case.”
(iii) Speculative Motive: This is the desire to hold money to take advantage of future investment opportunities. For example, if interest rates are expected to rise or prices of bonds are expected to fall, people may hold cash and wait.
(3b)
(PICK ANY FOUR)
(i) Loss of Investment Opportunity: Keeping too much cash means missing out on potential profits that could come from investing in productive ventures.
(ii) Reduction in Wealth Value: Inflation reduces the purchasing power of money. Over time, the same amount of cash buys fewer goods.
(iii) Increased Temptation to Spend: People who hold a lot of cash are more likely to spend carelessly on non-essentials.
(iv) Lack of Capital for Growth: Businesses holding excess cash may fail to expand, buy machines, or enter new markets, which limits growth.
(v) Opportunity Cost: Money not invested elsewhere is a lost opportunity to earn better returns from assets like shares or real estate.
(vi) Security Risk: Holding large amounts of cash increases the risk of theft, loss, or fire damage.
(vii) Lower Returns Compared to Investments: Cash earns less than bonds, stocks, or savings accounts. So it’s not profitable in the long run.
(viii) Slows Economic Activity: If too many people hoard cash, money doesn’t circulate in the economy. This can reduce demand and economic growth.
======================================
(4a)
(PICK ANY TWO)
(i) In capitalism, individuals own and control the means of production, while in socialism, the government owns and controls them.
(ii) Capitalism encourages competition, while socialism promotes cooperation and collective interest.
(iii) The profit motive drives capitalism, while socialism focuses on public welfare and equality.
(iv) Prices are determined by demand and supply in capitalism, while in socialism, prices are fixed by the government.
(v) Capitalism supports private ownership of property, while socialism discourages or limits private ownership.
(vi) Capitalism often leads to income inequality, while socialism aims to reduce the gap between the rich and the poor.
(4b)
(i) Private Ownership of Resources: In a free market economy, individuals and private businesses have the right to own and control the factors of production such as land, capital, and enterprises. The government plays little or no role in controlling property. Owners are free to use their resources as they choose, which encourages personal initiative and investment.
(ii) Price Determined by Demand and Supply: Prices of goods and services are not set by the government but are determined by the interaction of demand and supply in the market. When demand is high and supply is low, prices go up; when supply is high and demand is low, prices fall. This system ensures that goods are allocated efficiently based on market forces.
(4c)
(PICK ANY FOUR)
(i) Lack of incentive to work hard due to equal reward system.
(ii) Government may mismanage resources.
(iii) Bureaucracy can delay decision-making.
(iv) Limited consumer choice due to government control.
(v) High taxation to fund social programs.
(vi) Innovation may be discouraged due to lack of competition.
====================================
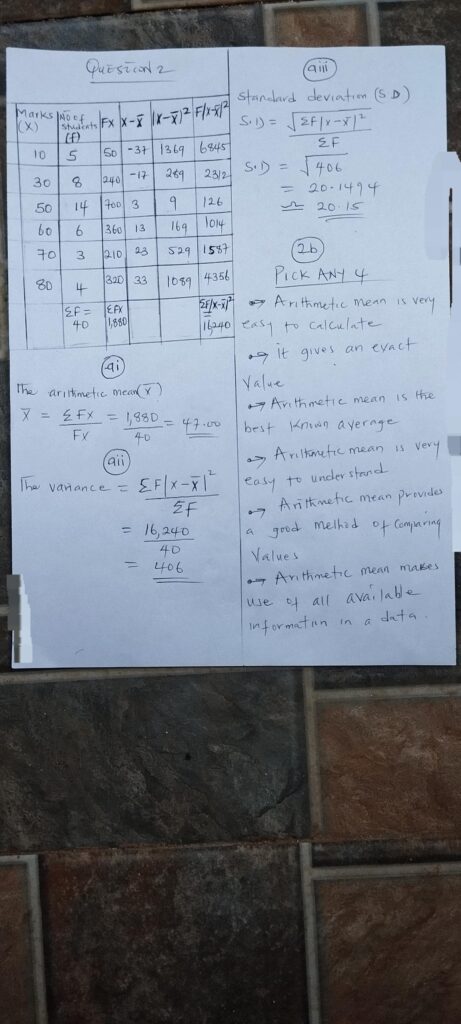
(6)
(PICK ANY FIVE)
(i) Provision of Basic Infrastructure: The government can promote industrialisation by building essential infrastructure such as electricity, good road networks, water supply, railways, and telecommunication systems. These are vital for transporting raw materials and finished goods, reducing costs, and making industries more efficient and competitive.
(ii) Access to Low-Interest Loans and Credit: Industries, especially small and medium enterprises (SMEs), often lack the capital to expand or upgrade. Government can encourage industrialisation by providing accessible and affordable loans through banks or special financial institutions. Grants and soft loans will reduce startup challenges for new industries.
(iii) Establishment of Industrial Layouts and Free Trade Zones: The government can create special areas like industrial estates, free trade zones, and export processing zones with ready infrastructure and tax incentives. These zones reduce overhead costs and encourage local and foreign investors to set up industries.
(iv) Investment in Technical Education and Vocational Training: A skilled workforce is key to industrial growth. Government can invest in polytechnics, technical schools, and training centres to equip citizens with practical and industrial skills needed by manufacturers and industries.
(v) Protection of Local/Infant Industries: To support new industries, the government can place tariffs on imported goods, offer subsidies, or introduce import bans on products that can be made locally. This protects young industries from foreign competition until they grow stronger.
(vi) Implementation of Friendly Industrial Policies: Government can introduce favourable laws and regulations such as tax holidays, reduced company taxes, and import duty waivers. These policies reduce the burden on industries and encourage private sector participation in industrial growth.
(vii) Encouragement of Local Raw Material Development: Industrialisation depends on raw materials. Government can encourage agriculture and mining sectors to produce and supply raw materials locally. This reduces dependence on imports and cuts production costs.
(viii) Security and Political Stability: No industry can grow in an unsafe environment. By ensuring peace, security, and stable political leadership, the government creates an enabling environment where investors feel confident to build and grow industries.
===========================================
(7a)
Balance of Payments (BOP) is a record that shows the total economic transactions between one country and the rest of the world over a specific period of time. It includes trade in goods and services, investments, and financial transfers
(7b)
(PICK ANY FIVE)
(i) Export Promotion: Government can encourage and support the production and export of local goods by giving incentives to exporters, reducing export duties, and improving infrastructure.
(ii) Import Restriction: Restricting the importation of non-essential goods through higher tariffs, import quotas, or outright bans can help reduce foreign exchange spending.
(iii) Currency Devaluation: Reducing the value of a country’s currency makes imports more expensive and exports cheaper, which can boost exports and reduce imports.
(iv) Foreign Loans and Aid: A country can seek financial assistance from international organizations or friendly nations to support its balance of payments position temporarily.
(v) Tourism Promotion: Encouraging tourism can help earn more foreign exchange as foreign tourists bring in money that boosts the country’s reserves.
(vi) Increase in Foreign Investment: Attracting foreign investors to invest in local businesses and industries can bring foreign exchange into the country.
(vii) Encouraging Remittances: The government can create incentives for citizens working abroad to send money home through official channels.
(viii) Import Substitution: Producing locally what is normally imported can help save foreign exchange and reduce dependence on foreign goods.
====================================
Neco 2025 Economics Question And Answer
(9a)
Debt servicing is the process by which a country makes regular payments to settle the interest and repay the principal amount borrowed through loans. These loans can be internal (borrowed within the country) or external (borrowed from foreign countries or international financial institutions like the IMF or World Bank). Failure to service debts on time can lead to loss of creditworthiness and reduced access to future funding.
(9b)
Gross National Product (GNP) is the total market value of all final goods and services produced in a given year by the nationals of a country, regardless of whether the production occurs within the country or abroad. It includes income earned by citizens and businesses abroad but excludes income earned by foreigners within the country.
(9c)
Disinflation refers to a decrease in the rate of inflation over time. It means that while prices are still rising, they are increasing at a slower rate than before. It is often a sign of effective economic policies aiming to stabilize the economy and control inflation. Disinflation should not be confused with deflation, which is an actual fall in the general price level.
(9d)
A surplus budget occurs when a government’s revenue exceeds its expenditure within a specific budget year. This means the government is earning more money than it spends on services, salaries, infrastructure, and other public needs. A surplus budget can be used to pay off national debt, build reserves, or invest in developmental projects.
(9e)
Poverty alleviation refers to all efforts made by the government or non-governmental organizations (NGOs) to reduce or eliminate poverty in a society. These efforts may include creating job opportunities, providing free or subsidized education and health care, giving grants or loans to small businesses, and running social welfare programs. The goal is to improve the standard of living and ensure equal opportunities for all citizens.
===================================
Neco 2025 Economics Question And Answer
(10a)
Localisation in industries refers to the concentration or grouping of similar or related industries in a particular geographical area or location. This happens when firms within the same industry choose to set up their operations close to each other in order to benefit from shared resources, infrastructure, labour, and markets.
(10b)
=Advantages=
(PICK ANY THREE)
(i) Availability of Skilled Labour: Firms enjoy access to a pool of trained and experienced workers who specialize in that particular industry.
(ii) Development of Ancillary Services: Support industries like transportation, maintenance, packaging, and finance are likely to grow around the area, improving efficiency.
(iii) Shared Infrastructure: Industries in the same location can share roads, electricity, water supply, and communication facilities, reducing individual costs.
(iv) Quick Access to Raw Materials and Suppliers: Localisation encourages suppliers to establish close to production centers, ensuring steady and cheap supply of raw materials.
(v) Knowledge and Innovation Sharing: Firms benefit from the free flow of ideas, technical know-how, and innovation when clustered together.
(vi) Market Expansion: A large concentration of industries attracts more buyers and sellers, creating a robust and ready market for goods and services.
=Disadvantages=
(PICK ANY TWO)
(i) Environmental Pollution: Concentration of industries in one area can lead to excessive pollution of air, water, and land.
(ii) High Competition: Too many firms in one place can lead to over-saturation of the market, reducing profits and survival chances for smaller firms.
(iii) Pressure on Infrastructure: Overpopulation of industries can strain local infrastructure like roads, housing, electricity, and water supply.
(iv) Risk of Regional Imbalance: Other regions may be neglected in terms of development, leading to inequality and underdevelopment elsewhere.
(v) Labour Exploitation: High demand for labour may lead to low wages or exploitation if regulations are not enforced.
(vi) Vulnerability to Disasters: If the area faces natural or man-made disasters (like flood, fire, or economic crash), all industries clustered there may collapse together.
===============================
(11a)
(PICK ANY TWO)
(i) A budget deficit occurs when government spending is more than revenue, while a budget surplus occurs when government revenue is more than spending.
(ii) Budget deficit leads to borrowing or debt accumulation, while budget surplus results in savings or reserve buildup.
(iii) Budget deficit may lead to inflation due to excessive government spending, while budget surplus may help control inflation.
(iv) Budget deficit may indicate poor financial management, while budget surplus may show fiscal discipline.
(v) Budget deficit is often associated with developing economies, while surplus is more common in developed or well-managed economies.
(vi) A budget deficit may reduce investor confidence, while a surplus may boost investor confidence.
(11b)
(PICK ANY FOUR)
(i) Mobilization of Capital: The stock exchange provides a platform where businesses and governments can raise long-term capital by issuing shares and bonds to investors.
(ii) Liquidity of Investments: It enables investors to convert their shares or securities into cash quickly, promoting flexibility and access to funds when needed.
(iii) Determination of Share Prices: The stock exchange helps determine the value of securities through the forces of demand and supply, providing fair and transparent pricing.
(iv) Encouragement of Savings and Investment: It encourages the public to save and invest in securities rather than keeping money idle, thus fostering economic growth.
(v) Economic Indicator: The stock exchange serves as a barometer of economic performance, reflecting changes in economic activities and investor confidence.
(vi) Risk Reduction through Diversification: It offers various investment opportunities which allow investors to spread their risk across multiple sectors and companies.
(vii) Facilitation of Mergers and Acquisitions: Companies use the stock market to raise capital or acquire other firms, promoting expansion and restructuring of businesses.
(viii) Regulation and Protection of Investors: The stock exchange operates under strict rules to ensure transparency, prevent fraud, and protect the interest of investors.
=======================================
Neco 2025 Economics Question And Answer
(12)
(PICK ANY FIVE)
(i) Improve Salary and Welfare Packages: One of the major reasons professionals leave Nigeria is poor remuneration. The government should provide competitive salaries, allowances, and welfare packages that match international standards, especially for doctors, engineers, and lecturers.
(ii) Upgrade Infrastructure and Work Environment: Lack of modern equipment, power supply, and good office conditions often frustrate professionals. Upgrading hospitals, research labs, universities, and ICT systems will motivate skilled workers to remain and contribute locally.
(iii) Create More Job Opportunities: Many skilled Nigerians leave the country due to unemployment or underemployment. The government should promote job creation through industrialization, support for SMEs, and strategic investment in key sectors like tech, agriculture, and health.
(iv) Promote Political Stability and Good Governance: Political instability, corruption, and insecurity make people lose faith in the system. By ensuring good governance, transparency, and justice, citizens will feel safer and more motivated to remain in the country.
(v) Encourage Diaspora Return Programs: Introduce attractive policies to encourage Nigerians abroad to return home, such as tax breaks, startup grants, and resettlement support. Countries like India and China have successfully used this model.
(vi) Invest in Quality Education and Research: When universities are properly funded, lecturers paid on time, and academic strikes ended, professionals will be encouraged to stay and build careers in Nigeria.
(vii) Recognize and Reward Excellence: Introduce national recognition and reward systems for top-performing professionals in every field. Celebrating achievements boosts morale and reduces the urge to migrate.
(viii) Partner with the Private Sector: The government should work with companies to develop innovation hubs, internship programs, and mentorship schemes that retain young talents within the country.
(ix) Tackle Insecurity: Widespread insecurity drives professionals to seek safer environments abroad. Strengthening national security and law enforcement will make Nigeria a more attractive place to live and work.…….





Wow thanks for the help
How did you get the help from this people
Please help me I need help please sir
WOW THANK YOU FOR HELPING ME AND MY BOYFRIEND
CAN U HELP ME
Thanks but please which time ⏲️ did you drop it
Pls i need economics answer
how can u be giving me answer
The Same Thing I Ask for
OOH GOD U GIVE CHARITY IN THIS PEPAR
Pls can u send me the question to this
number abeg 09030053xxxx if u send the question I will help u with the solution
NECO EXAMINATION 2025
Hi. gd morning, pls i need neco economics obj and essay answer this morning. How do i get it. Thanks
I need economics answer
i need economics pin for the first paper
Neco answer for economic obj and essay 2025
Economic question and anwser please
show be how to get this pin
ok 3237 this is the pin
please i need economic answer
Please help us for economics
How to check answer
Pls i need economic answers and question
how can i check waec result
PHYSICC OBJ
How can seen physic question
hi thank u very mush